Basics
What is container?
- its layers of images
- Linux based image
- and application image on top
What is Docker?
It manages containers!
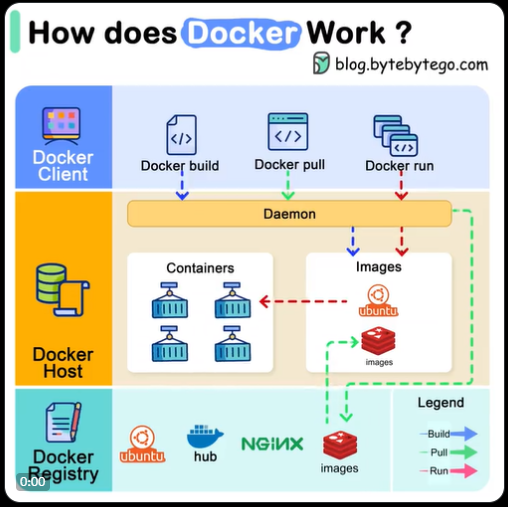
What is Docker Images?
It is kind of a readonly filesystem or say CD Disk like a ISO from which we can run a container.
How to create Image?
Option 1: Using Dockerfile
Dockerfile
FROM Ubuntu
1. OS - Ubuntu
RUN apt-get update
2. Update apt repo
RUN apt-get install python
RUN pip install flask
3. Install dependencies using apt
RUN pip install flask-mysql
4. Install Python dependencies using pip
COPY . /opt/source-code
ENTRYPOINT FLASK_APP=/opt/source-code/app.py flask run
docker build Dockerfile –t yourusername/my-custom-app
docker push yourusername/my-custom-app
This will upload your dockerfile to docker registory online such as dockerhub.io
Docker Registry
docker run nginx
In this case nginx is repository name where it pull from the remote location such docker hub.
When user give image name to pull it actually expect account name and repo name like this:
docker run nginx/nginx
In this case first nginx is account name and second is repo name. When user type of only one name i.e. docker run nginx it assumes that both account name and repo name is that same name.
Public Registry
There are popular public docker repositories:
- gcr.io - google repository
- hub.docker.io - dockers official repository
Private Registry
There are self hosted or private registries to chose from incase you dont want public exposure. Many cloud providers gives you private registries :
- AWS
- Azure
- JCP
To run a container from private registry you need to first login to with following command :
docker login private-registry.io
then you can run your private repository:
docker run private-registry.io/apps/internal-app
Deploy private registry
What if you running your application on premise and dont have private registry how do you deploy your own private registry within your organization:
The docker registry is itself is an application and it available inside docker image. The name of the image is registry. It exposes the api on port 5000.
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --name registry registry:2
Now that you have your custom registry running on port 5000 on how do you push your own image to it.
docker image tag my-name localhost:5000/my-image
docker push localhost:5000/my-image
Now you can pull this image anywhere within this network with server name i.e. localhost or ip address of the host.
docker pull localhost:5000/my-image
docker pull 192.168.56.100:5000/my-image
Example:
To push some images into our locally hosted registry we can first pull then, tag them and then push them like this:
Pulling:
docker pull nginx:latest
then Tagging:
docker image tag nginx:latest localhost:5000/nginx:latest
and finally push it:
docker push localhost:5000/nginx:latest.
To check the list of images pushed , use: curl -X GET localhost:5000/v2/_catalog
To remove all locally non running images
docker image prune -a
Now we can pull images from our registry-server as well. Use docker pull [server-addr/image-name] to pull the images that we pushed earlier.
In our case we can use: docker pull localhost:5000/nginx