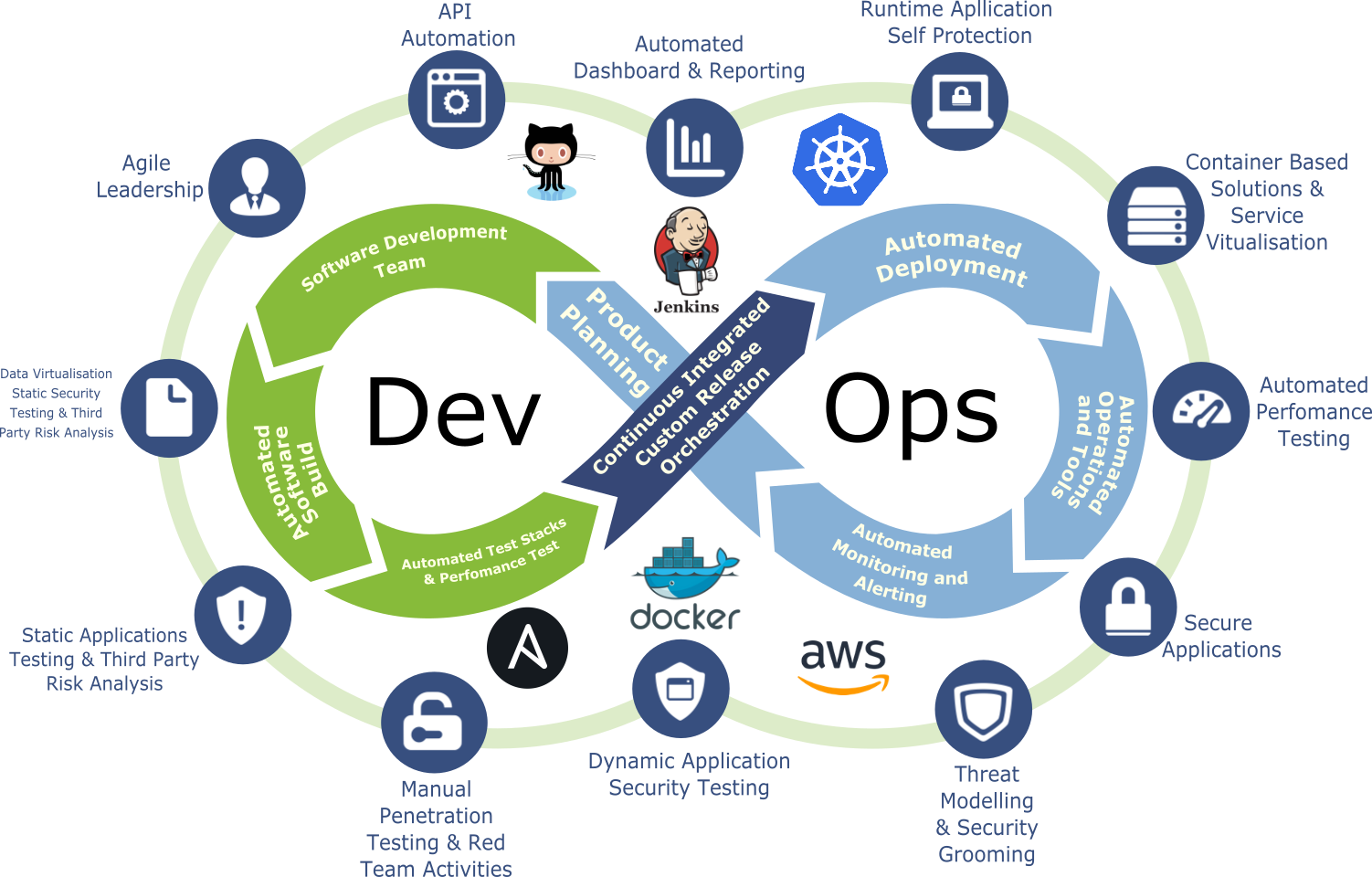
1. General DevOps Interview questions
The questions in this section are meant to test your basic understanding of DevOps. As a DevOps engineer you should be familiar with concepts and spirit of DevOps process and principles.
1.1 Why do you need DevOps?
In the most basic terms, DevOps allows companies to achieve seamless software delivery. This is why major companies like Google, Etsy, and Amazon have used DevOps to achieve insane levels of performance. DevOps allow you to do thousands of code deployment per day without sacrificing stability and reliability.
1.2. What are some of the top DevOps tools?
Some of the most popular DevOps tools are:
- Jenkins, which is a Continuous Integration tool
- Nagios, which is a Continuous Monitoring tool
- Docker, which is a Containerization tool
- Selenium, which is a Continuous Testing tool
- Git, which is a Version Control System tool
1.3. What are the advantages of DevOps?
DevOps provide many technical benefits like continuous software delivery, less complex problems, and faster resolution. It also provides many business benefits like stable operating environments and faster delivery of features.
1.4. What are some of the core benefits of using DevOps?
The DevOps methodology is highly flexible, which means that it can adapt to changes easily. It also increases collaboration between the development team and the operation team. You can also increase efficiency by using automation and continuous integration. All of this means that customer satisfaction is also increased.
1.5. How can you use DevOps in real-life?
DevOps is really useful for a lot of industries. One of the best examples of a company transforming its fortunes with the help of DevOps is the case of Etsy. Etsy was frequently struggling with slow site updates that also resulted in site crashes. It affected almost all of Etsy’s customers. But with the help of a new technical management team, Etsy transformed into an agile approach. These days, it has a fully automated deployment pipeline. Its continuous delivery practices have also resulted in more than 50 deployments per day with very few disruptions.
1.6. What, according to you, is the most important thing that DevOps helps us to achieve?
If you ask me, the most important thing that DevOps helps achieve is that it allows us to get changes into production as quickly as possible. It minimizes risks in software quality assurance and compliance. This is also the main objective of DevOps. But it also provides many other positive effects.
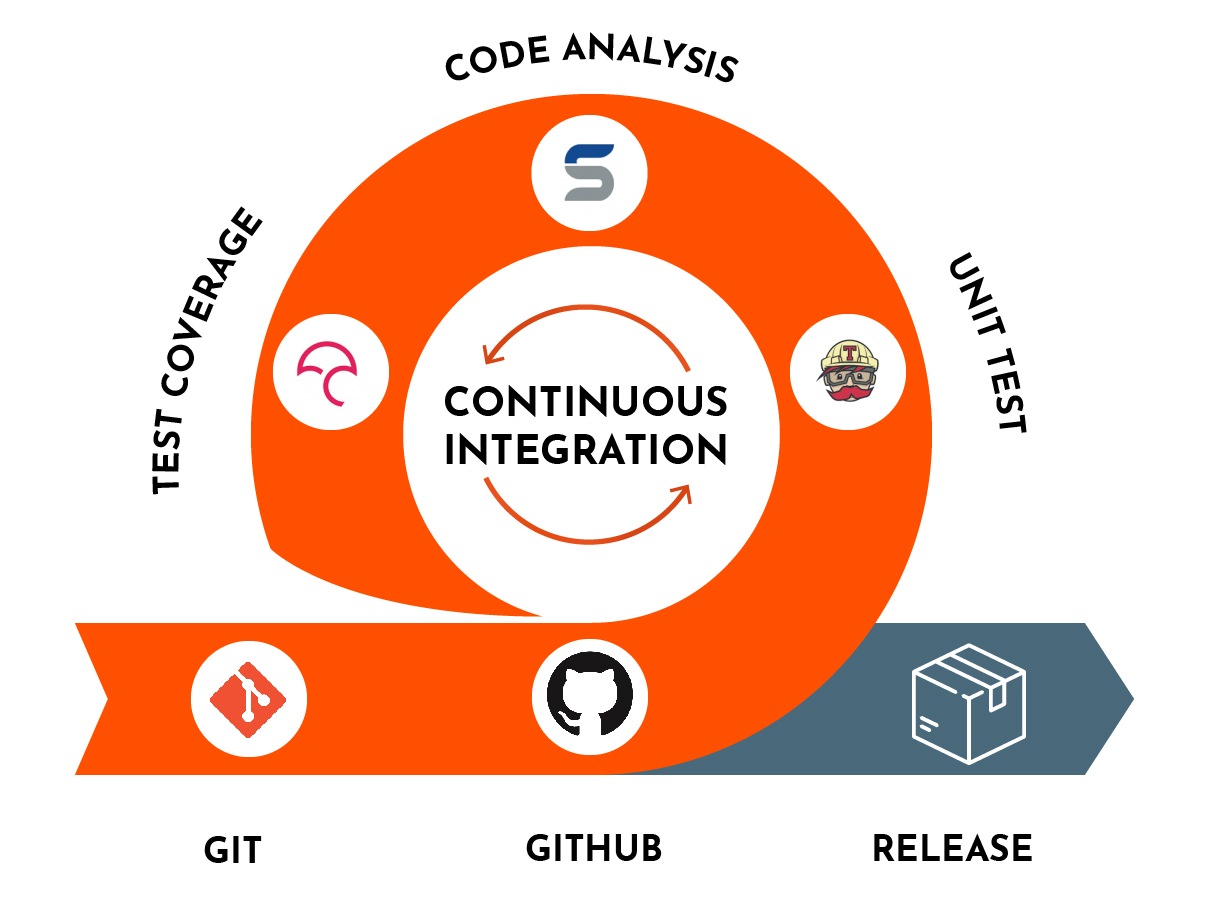
2. Continuous Integration Interview Questions
Pipeline development and management is one of the key job for DevOps Engineer and if you want to succeed in DevOps interview you should be familiar with Jenkins, TeamCity or similar tool as well the concept and practical of creating and maintaining build and deployment pipelines using tools like Jenkins, Docker, Ansible, and Puppets.
2.1. What do you mean by Continuous Integration?
Continuous Integration is basically a practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared registry for easy collaboration. This allows problems to be detected early.
2.2. What are the requirements for Continuous Integration?
For successful Continuous Integration, you should maintain a code repository and automate the build. You should also make sure that all the developers commit to the baseline every day. You should make it easy to get the daily deliverables so that everyone can see the latest results.
2.3. How will you move Jenkins from one server to another?
First, you can move the job from one installation of Jenkins to another by copying the job directory. Then you should rename the existing job, You can do this by renaming the directory. You can also make a copy of the existing job.
2.4. How can you set up a Jenkins job?
First, you should go to the Jenkins top page, select New Job, and then select Build a freestyle software project.
2.5. What, according to you, are some of the useful plugins in Jenkins?
Some of the most important plugins are Maven 2 Project, HTML Publisher, Amazon EC2, Copy Artifact, Green Balls, and Join. These are some of the most useful plugins.
2.6. How can you secure Jenkins?
There are many steps for securing Jenkins. For starters, you can make sure that Jenkins is fully integrated with the company’s user directory with the appropriate plugin. You can also ensure that global security is on. You also have to automate the process of setting privileges in Jenkins with the help of a custom version-controlled script. You can limit access to Jenkins folders as well as periodically run audits. You also have t make sure that the Project matrix is tuned on to fine-tune access.
3. Continuous Testing Interview Questions
This is the next area where DevOps are really tested as one of the job for DevOps is to maintain code quality and automation testing, code analysis, and automation build quality checks are quite important. Familiarity with tools like SonarQube can be great help to pass this round.
3.1. What do you mean by Continuous Testing?
Continuous Testing is basically a process of running automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline. By doing this, you will be able to get immediate feedback on the associated business risks of the latest build.
3.2. What do you mean by Automation Testing?
Using Test Automation, you can automate the process of testing an application or a system. You can use separate testing tools which will allow you to create test scripts that can then be executed.
3.3. What are the advantages of Automation Testing?
Automation Testing allows you to do parallel execution and also encourages unattended execution. It also increases accuracy as well as saves time and money. It also supports the execution of repeated test cases.
3.4. Why is Continuous Testing so important?
Continuous Testing allows you to test any changes made in the code immediately. Continuous Testing also facilitates more frequent and good quality releases.
3.5. What are some of the key elements of Continuous Testing?
Some of the most important elements of continuous testing are risk assessment, policy analysis, requirements traceability, advanced analysis, test optimization, and service visualization.
- Risk Assessment is made up of mitigation tasks, technical debt, quality assessment, and test coverage optimization to make sure that there is adequate progress.
- Policy Analysis is used for making sure that all processes align with the company’s business and compliance goals.
- Requirements Traceability ensures that true requirements are met and that rework is not required. It can also identify which requirements are at risk, working as expected, or require further validation.
- In Advanced Analysis, automation is used in areas such as static code analysis, change impact analysis, and scope assessment. This is useful for preventing defects in the first place as well as accomplishing more with each iteration.
- Test Optimization helps ensure that tests yield accurate outcomes and provide adequate findings. Different aspects of Test Optimization are Test Data Management, Test Optimization Management, and Test Maintenance.
- Service Visualization helps ensure that real-world testing environments are accessible. It also enables access to the virtual form of the required testing stages. It is useful for cutting waste time testing environment setup and availability.
3.6. What are some of the benefits of using Selenium?
I have worked extensively with Selenium and some of its advantages are that
- It has a large user base and amazing communities
- It is free and open-source.
- It has great platform compatibility and works well with Windows, Linus, and Mac.
- It has the cross-browser capability and works with Firefox, Google Chrome, and Internet Explorer.
- It supports multiple programming languages like Java, Ruby, C#, Python, and Pearl.
- It supports distributed testing.
- It has regular and fresh repository developments.
3.7. What can you tell us about Selenium IDE?
Selenium IDE can be seen as an integrated development environment that is useful for Selenium scripts. It can be implemented as a Firefox extension and you can use it to edit, record, and debug tests. The Selenium IDE includes the entire Selenium Core, which allows you to easily record and playback tests in actual environments. It has to autocomplete support as well as the ability to move around commands pretty quickly. You can say that Selenium IDE is the perfect environment for creating Selenium tests as it provides the perfect environment.
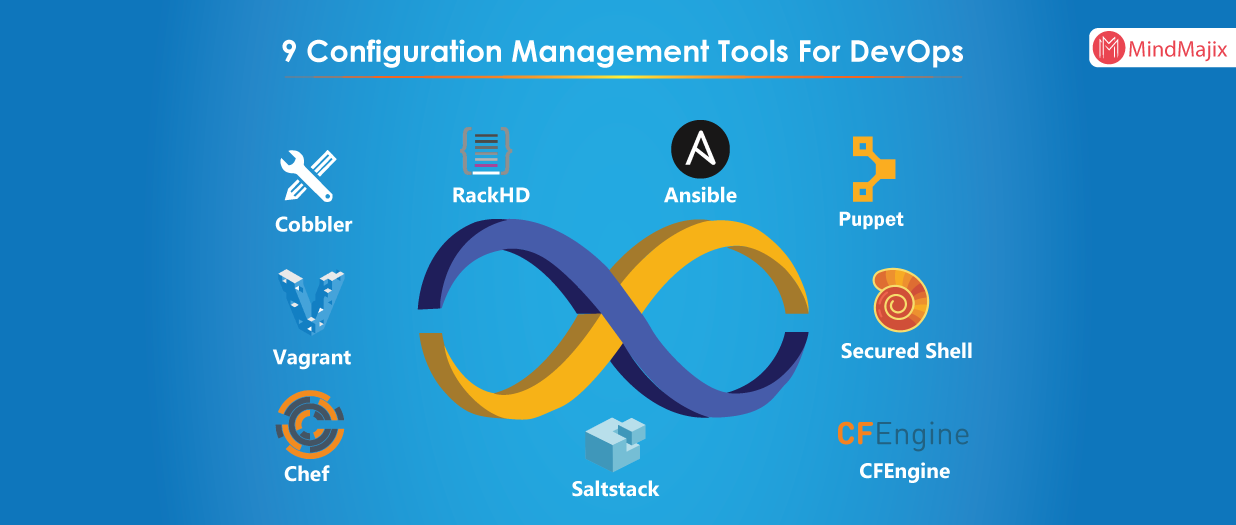
4. Configuration Management Interview Questions
Automation of configuration and management is another big responsibility of DevOps Engineer, hence preparing Configuration Automation and management question is quite important for DevOps. This section shares common Configuration management questions.
4.1. Why should you focus on Configuration Management?
Configuration Management allows you to improve performance and revise capability. You will be able to increase reliability, and maintainability, as well as extend the life of your application. You will also be able to reduce risks, costs, and liability.
4.2. What do you understand by ‘Infrastructure as Code’?
It is basically a type of IT infrastructure that you can use to automatically manage your provisions through code. There is no need for manual testing.
4.3. Which community tools can you use to make Puppet more powerful?
You can use Git and Puppet’s Code Manager app to make sure that the code is in accordance with best practices. You can also run all the Puppet changes through the continuous integration pipeline using the beaker testing framework.
4.4 What is the Puppet Module?
A Puppet Module is basically a collection of Puppet Manifests and data that have a very specific directory structure. It is useful for organizing your Puppet code as you will be able to split your code into different Puppet Manifests.
5. Containerization and Virtualization Interview Questions
Containerization is nowadays become an essential part of building and deploying application. Most of the application are deployed by creating Docker images on Cloud and they are managed by Kubernetes, which can automatically start, stop, and scale Docker containers. Having a solid knowledge of how Containers works and how to containerize an application can be really good skill for DevOps Engineer, familiarity with Docker and Kubernetes can be really great help.
5.1. What do you mean by containers?
Containers can be used to provide a consistent computing environment. It is made up of an entire runtime environment. It has an application, all of its dependencies, libraries, and binaries. It also has all the configuration files needed to run the application.
5.2. What are the advantages of Containerization?
Containers are lightweight and have better resource utilization. It can also provide real- time provisioning and scalability. It also has unlimited performance.
5.3. What is a Docker image?
Docker images are used to create Docker containers. Docker images can be created using the build command. When an image is selected and starts to run, it will produce a container.
5.4. What do you know about Docker Hub?
Docker Hub is basically a cloud-based service that you can use to build images, test them, store manually published images, and deploy images to your hosts. It also gives you a centralized resource for storing your container images.
6. Kubernetes - Basic Kubernetes Interview Questions
For easy access, I have divided this article into three sections. The first section consists of basic Kubernetes interview questions. In this section, you will learn about topics like Autoscaling, Load Balancing, and Data Volumes. The second section consists of interview questions related to the architecture of Kubernetes. This section covers topics like Kube-proxy and master node. The third section deals with some multiple-choice questions. Here, you will get some practical exposure as well as enhance your quick thinking. I have also tried to cover to basic kubectl command you can use to interact with pods and services. I have no doubt that the interview questions in this article will help you to land your dream job.
6.1. What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is basically a container-management tool that is open-source and can scale, descale, and deploy containers. It is similar to Docker and was introduced by Google. This means that it has an interactive community and works well with all the cloud providers. We can say that Kubernetes is not just a containerization platform, but a platform that provides multi-container management solutions.
6.2. How is Kubernetes similar to Docker?
A Docker image can be used to build runtime containers and it also provides lifecycle management of containers. Kubernetes come in when these individual containers need to communicate with each other. What this essentially means is that Docker can be used to build individual containers and Kubernetes can be used to allow these individual containers to communicate with each other. Another important thing to note here is that containers running on multiple hosts can be connected to each other and linked using Kubernetes.
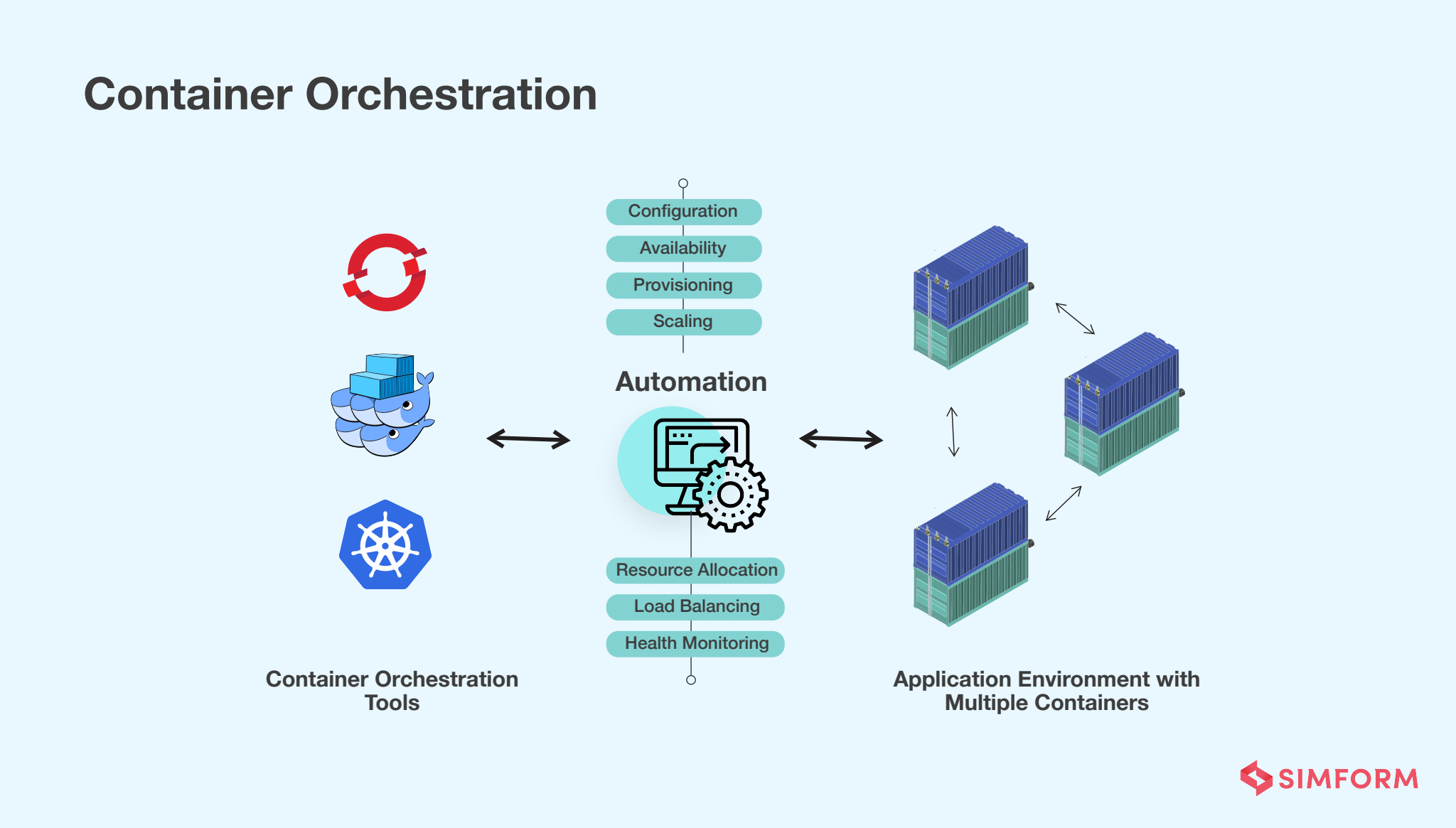
6.3. What is Container Orchestration?
Container Orchestration effectively means that all the services inside the individual containers are working together seamlessly to meet the needs of the server. There are many microservices inside each container, and it is impossible for these microservices to communicate with each other without Container Orchestration. Container Orchestration creates harmony among containers by seamlessly allowing individual containers to work together and met the goal of a single server.
6.4. Why do you need Container Orchestration?
When you have 4 or 5 micro services that perform various tasks for a single application, you can put these microservices inside separate containers. But you need to make sure that these containers interact with each other. So Container Orchestration becomes useful in such cases. Basically, Container Orchestration is essential for making sure that containers communicate effortlessly with each other. There are also many challenges that can crop up if you do not use Container Orchestration. So Container Orchestration can be used to overcome these challenges.
6.5. What are some features of Kubernetes?
Kubernetes offer some amazing features like Automated Scheduling, Self-Healing Capabilities, Automated Rollouts and Rollbacks, Horizontal Scaling, and Load Balancing. The automated scheduler can be used for launching containers on cluster nodes. Self-Healing Capabilities allow rescheduling, restarting, and replacing of dead containers. Kubernetes also supports automated rollouts and rollbacks for containers. Kubernetes can also scale up and scale down applications according to your requirements.
6.6. What is the Containerized Deployment process in Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is basically cloud-agnostic. What this means is that it can run on basically any cloud provider. This effectively simplifies the process of Containerized Deployment since the is no need for anything big like multiple hosts for load balancing.
Kubernetes can also run on any cloud platform since it is cloud-agnostic. For example, if you have a number of containers running on multiple hosts, all of these containers may have to communicate with each other. For this, you need something big that can be used for load balancing, scaling, and monitoring the containers.
6.7. What is Google Container Engine?
Google Container Engine is a managing platform for Docker Containers and clusters. It is open-source and supports only those containers that run inside Google’s own cloud services. Google Container Engine is also known as GKE. One important thing to note here is that the Google Container Engine supports only those containers that run on its own public cloud platforms.

Bonus Questions
1. What is Heapster?
Heapster is basically a data aggregator that is present cluster-wide. It is provided by Kubelet running on each node. It can also be seen as a container management tool that Kubernetes supports natively. It runs just like any other pod on the cluster. What this means is that it discovers all the nodes in a cluster and queries usage information from the Kubernetes cluster present on every node.
2. What is Kubectl?
Kubectl can be seen as a platform that can be used for passing commands to the cluster. It also provides the CLI command for running Kubernetes commands against the Kubernetes cluster. It also has various ways and means for creating and managing the Kubernetes component.
3. What is Minikube?
Minikube can be seen as a tool that makes it easier to run Kubernetes locally. It runs a single-node Kubernetes cluster inside a virtual machine.
4. What is Kubelet?
Kubelet is basically an agent service that runs on each and every node and also allows communication between the slave and the master. It essentially works on the description of containers that are provided to it in the PodSpec. It also makes sure that the containers that are described in the PodSpec are healthy and running.
5. What can you tell us about a node in Kubernetes?
A node in the Kubernetes cluster can be seen as the main worker machine. Nodes are also known as minions. Nodes can run on physical machines or virtual machines. It provides all the necessary services for running pods. Nodes in the Kubernetes system are managed by masters.
7. Kubernetes Architecture Interview Questions
7.1. What can you tell us about Kube-proxy?
Kube-proxy is basically a network proxy that is made up of configured services in Kubernetes API. It runs on each and every node and can do packet forwarding across multiple services. Kube-proxy can also run on each and every node. It can do simple TCP/UDP packet forwarding all across the backend network service. A Docker-linkable compatible environment can also provide the various IPs and ports that can be opened using a proxy.
7.2. What can you tell us about the different components of Kubernetes Architecture?
Kubernetes architecture is made up of 2 main components - the master node and the worker node. The master node is made up of the Kube-controller-manager, Kube- apiserver, and the Kube-scheduler. The worker node has kubelet and Kube proxy.
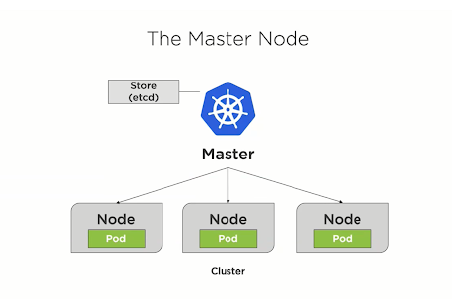
7.3. How does the master node work in Kubernetes?
The nodes are made up of containers and the Kubernetes master controls these nodes. The individual containers are housed inside pods and each pod can have a number of these containers. The Kube-apiserver makes sure that there is communication between the pods and the master node. The Kubernetes master controls all the nodes and the containers that are present inside the nodes. The individual containers are housed inside pods. Inside each pod, you can have a large number of containers depending on your requirements. These pods can be deployed using the user interface or the command-line interface. The pods are allocated to different nodes based on the resource requirements. The Kube-apiserver can be used for making sure that there is always communication between the Kubernetes node and the master component.
7.4. What do you know about the Kubernetes controller manager?
The controller manager is basically a daemon that embeds controllers and works in namespace creation and garbage collection. It is also responsible for communicating with the API server and managing the end-points. The master node runs multiple control processes. But all these processes are compiled together to run as a single process. This process is known as the Kubernetes controller manager. The Kubernetes controller manager is responsible for communicating with the API server and making sure that the end-points are managed. There are different types of controller managers running on the master node. The node controller manages the status of a node like creation, updating, or deletion. The replication controller maintains the number of pods for each and every replication object. The service account and token controller can be used for creating default accounts as well as API access tokens for creating new namespaces. The endpoints controller takes care of all the endpoint objects like services and pods.
7.5. What is ETCD?
ETCD is a distributed key-value store that coordinates distributed work. It is written in the Go programming language. It stores the configuration data of the Kubernetes cluster. ETCD can also be used for storing the configuration data of the Kubernetes cluster that represents the state of a cluster at any point in time.
7.6. How does the Load Balancer work in Kubernetes?
A load balancer is a common and standard way of exposing service. Kubernetes offer customers two types of load balancer - the internal load balancer and the external load balancer. The internal load balancer allocates pods with the necessary configuration while the external load balancer directs the traffic from the external load.
7.7. What is Ingress Network?
Ingress Network is basically a collection of rules that is an entry point to any Kubernetes cluster. It is an API object that manages access to the services inside a cluster. It is the most powerful way of exposing service.
Bonus Questions
1. What are the different types of services Kubernetes offer?
The Cluster IP can be used for exposing the service on a cluster-internal IP. It means that the service will only be reachable from within the cluster. This is the default service type. The Node Port can be used for exposing the service on each node’s IP at a static port. A Cluster IP service to which a Node Port service will route is automatically created. The Load Balancer exposes the service externally by making use of a cloud provider’s load balancer. Services to which the external load balancer will route are automatically created. The External Name maps the service to all the contents of the external name. There is no proxying of any kind during this setup.
3. Multiple-Choice Questions
3.1 Where is the Kubernetes Cluster data stored?
- A. Kube-apiserver
- B. Kubelet
- C. ETCD (Correct)
- D. None of the above
3.2 Which of the following is a Kubernetes Controller?
- A. Replicaset
- B. Deployment
- C. Rolling Updates
- D. Both A and B (Correct)
3.3 Which of the following are core Kubernetes objects?
- A. Pods
- B. Services
- C. Volumes
- D. All of the above (Correct)
3.4 On which node does the Kube-proxy run?
- A. Master Node
- B. Worker Node
- C. Both A and B (Correct)
- D. None of the above
3.5. Which of the following was introduced in Kubernetes version 1.8?
- A. Taints and Tolerations (Correct)
- B. Cluster Level Logging
- C. Secrets
- D. Federated Clusters
3.6. Which handler is invoked by Kubelet to check if a container’s IP address is open or not?
- A. HTTPGetAction
- B. ExecAction
- C. TCPSocketAction (Correct)
- D. None of the Above